The right selection of bundle extractors is essential for the safe, quick handling of tube bundles in refineries, chemical plants, and power plants. This comprehensive guide will clarify how self-propelled bundle extractor utility is maximized by understanding current market trends and technical specifications. Our primary focus is securing operator safety, reducing downtime, and improving productivity even in the most challenging systems.
Understanding optimal construction, control systems, hydraulic options, and equipment choices enables informed comparisons between industry-leading solutions. Modern portable options feature joystick-controlled remote operation, delivering precise, performance-oriented handling capabilities.
Understanding Bundle Extractors
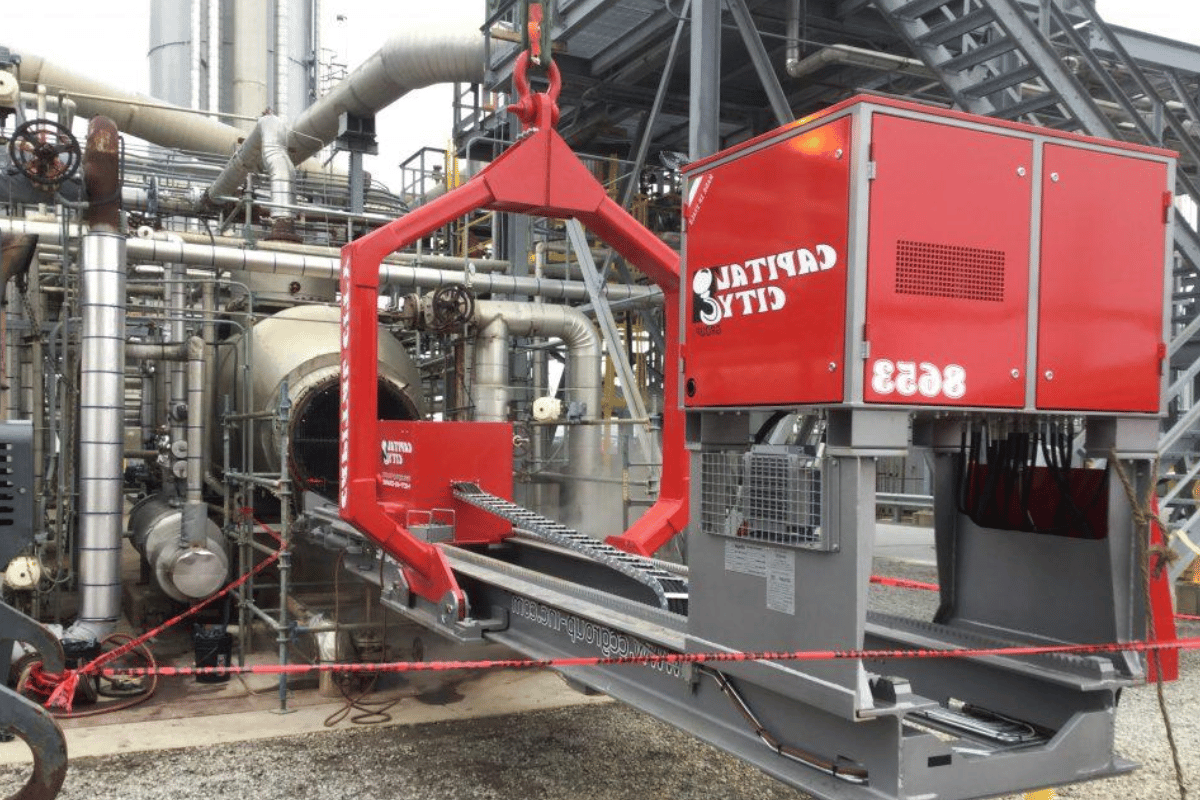
Bundle extractors are specialized maintenance equipment designed for pulling or inserting tube bundles from shell-and-tube heat exchangers. Modern bundle extractors integrate hydraulic power and control systems capable of handling heavy bundles measuring multiple tons without damaging the exchanger or endangering operators. The equipment typically features wheel sets or skid mounts enabling it to pull and push bundles along defined distances while accommodating maximum height requirements. Versatile operational design reduces turnaround time, enhances operator safety, and improves overall efficiency in routine and turnaround maintenance work.
What is a Bundle Extractor?
A bundle extractor is a hydraulic tube bundle extractor designed to grip, pull, and reinstall tube bundles with controlled tensioning. It provides precise alignment to maintain even load distribution and smooth operation during extraction from exchangers and tube transportation. With hydraulic power pack units generating force through control mechanisms ranging from simple manual valves to sophisticated remote-controlled systems, refinery operators can steer, position, and operate the equipment while minimizing damage to exchanger shells. Properly configured extractors reduce labor-intensive processes while decreasing handling time and enabling more proactive maintenance.
Types of Bundle Extractors
Bundle extractors come in several configurations, each suited to different operational requirements:
Skid-mounted units: Supported by hydraulic lines and systems for stationary operations
Truck-mounted hydraulic lifts: Used for handling specific maintenance issues related to sound, leaks, and erosion
Crane-assisted systems: Combine external lifting equipment with extraction capabilities
Self-propelled extraction equipment: Complete cradle units with integrated drive, control, and hydraulic systems
Main Features of Self-Propelled Bundle Extractors (SPBE)
The Self-Propelled Bundle Extractor (SPBE) represents the pinnacle of modern extraction technology, offering:
Hydraulic Power Pack
Integrated unit providing controlled force generation
Wheel Drive System
Enables mobile operation and precise positioning
Joystick Remote Control
Enhanced operator protection through remote operation
Precision Steering
Additional focus on asset protection and control
Technical Specifications: Standard self-propelled models specify tensile force capacity up to and beyond 25 tons, with high efficiency in extracting, pulling, and pushing bundles to maximum operational heights. Modern SPBE variants feature modular accessories integrating advanced safety interlocks with operator-friendly design ensuring reliable function.
Heavy-Type Bundle Extractors in Industry
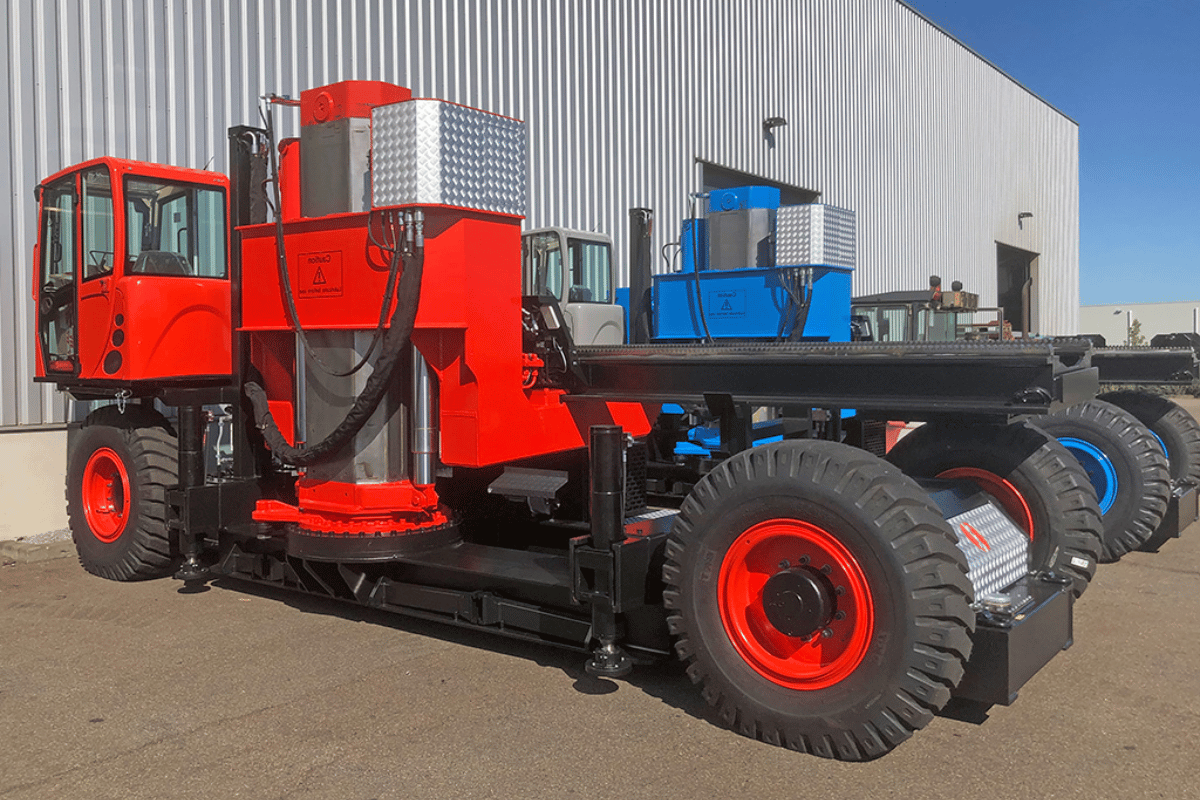

Heavy-type bundle extractors serve as essential maintenance equipment for refineries, petrochemical plants, and power stations, positioning the extraction of the most challenging bundles as routine day-to-day operations. This technology is built with robust construction, elevated tensile force ratings, and hydraulic power units sized for continuous-duty extraction. They are typically self-powered, with SPBE design integrating wheel drive, steering, and control to ensure successful bundle extraction over extended distances while accommodating height variations. Manufacturers provide technical data including maximum height specifications, greater than 25-ton capacity, thrust capability, and remote-controlled safety features offering operator protection and reliable operation.
Characteristics of Heavy-Type Bundle Extractors
A heavy-duty self-propelled hydraulic tube bundle extractor combines powerful hydraulics with precise control techniques to simultaneously extract, pull, and push tube bundles under heavy loads. Key characteristics include:
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Construction | Rigid build with balanced weight distribution and stable chassis |
| Tensile Force | Minimum 25 tons with full stroke pulling and pushing capability |
| Lifting Capacity | Tens of feet vertical reach |
| Control System | Proportional control valves with remote joystick operation |
| Operation | Drive, speed control, and adjustable clamping efforts |
Technical documentation for self-propelled units extends to driving wheel specifications, operational range, and maximum height tolerances handled by the bundle extractor.
Benefits of Heavy Equipment
Enhanced Reliability: Higher tensile forces provide assurance against equipment damage and operational failures. Improved reliability in moving heavily fouled tube bundles significantly reduces downtime and rework requirements.
Mobility and Versatility: Self-propelled bundle extractors offer mobility allowing one piece of equipment to service various exchangers with minimal setup time.
Operator Safety: Remote control joysticks greatly enhance operator safety by distancing personnel from line-of-fire hazards while maintaining precise control.
Hydraulic System Optimization: High efficiency at maximum height and stroke maintained without overheating, sustaining high pressure throughout operations.
Cost Effectiveness: Better operation yields fewer lifts, reduced rigging requirements, and lower cost per bundle due to improved handling consistency.
Typical Conditions of Use
Heavy-duty self-propelled bundle extractor systems excel in demanding applications including:
Heavy turnarounds against large shell-and-tube exchangers in refineries
Coke and crude unit maintenance requiring high-capacity extraction
Power plant condensers with seized or extremely heavy bundles
Congested pipe rack environments with limited operating space
Bundles with heavy fouling requiring deep penetration during reinstallation
The self-propelled configuration provides clear steering capability in narrow passages with minimal clearance requirements. Equipment such as Peinemann's heavy-duty SPBE units handle bundles with severe fouling, maintain control during operations, and ensure safety through verified technical specifications including height limits, tonnage capacity, and transport options.
Technical Data and Specifications
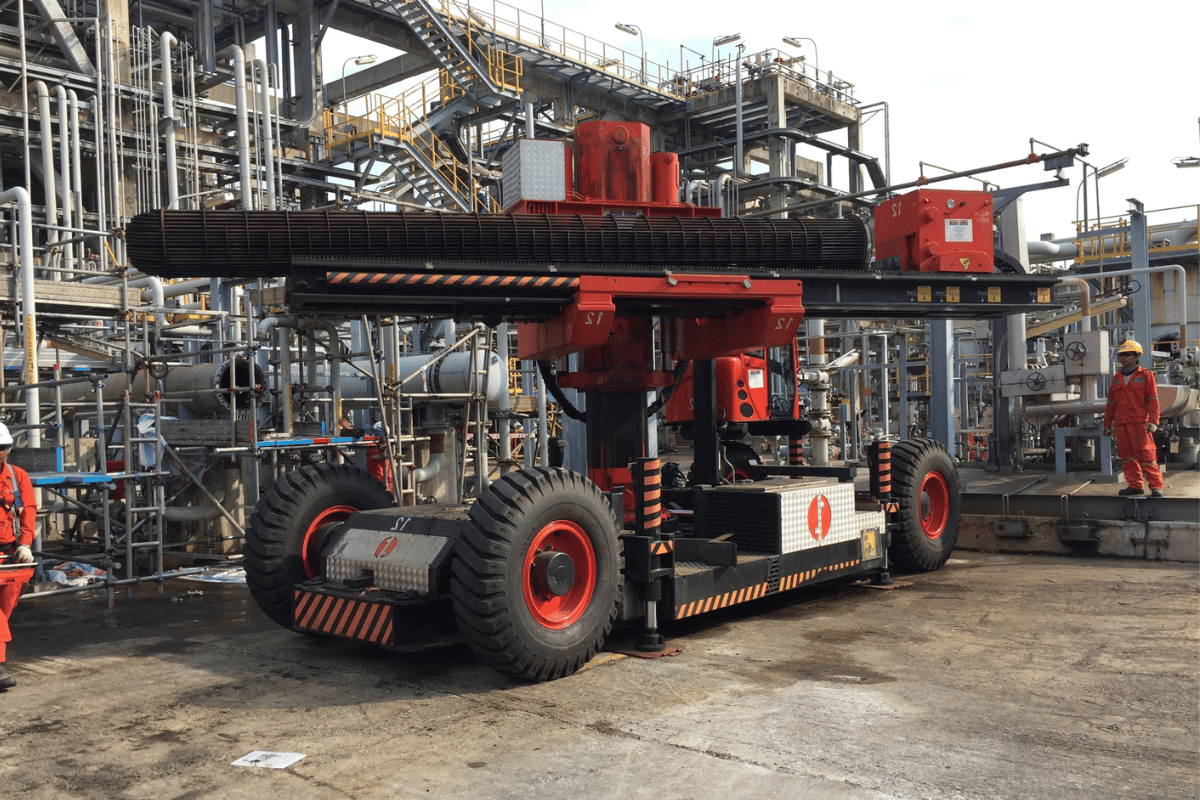
Technical data for self-propelled bundle extractors is essential for guaranteeing operational safety, efficient handling, and predictable extraction results. Important parameters include tensile force ratings up to and possibly exceeding 25 tons, maximum lifting distances measured in meters, wheel traction specifications, and required steering radius. Modern hydraulic tube bundle extractors directly integrate hydraulic power pack units with proportional directional control allowing smooth, controllable movements under load conditions. Properly configured apparatus can push or pull entire tube bundles with minimal shock to the exchanger or risk to personnel. Manufacturers like Peinemann Equipment issue self-propelled data sheets demonstrating equipment performance under extreme bundle conditions.
Key Specifications to Consider
When evaluating a self-propelled bundle extractor, define these critical parameters:
Documentation requirements include:
Maximum height specifications
Gradient slope ascending capability
Wheel axle-load distribution for chassis stability
Control performance including radio link latency and joystick response
Cycle times, energy consumption, and efficiency metrics
Outstanding equipment suppliers provide verifiable test data proving steering capability, operational range, and performance against rated tensile force specifications.
Comparative Analysis with Traditional Extractors
| Feature | Traditional Extractors | Self-Propelled Bundle Extractors |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | Requires external lifts and rigging | Fully integrated mobility with steering |
| Setup Time | Time-consuming with multiple rigging steps | Faster setup, ready for operation quickly |
| Operator Safety | Increased line-of-fire exposure | Remote joystick control minimizes risk |
| Tensile Strength | Variable, often limited | Up to 25+ tons with stability |
| Efficiency | Multiple exchangers require repositioning | Service multiple units per shift |
| Cost Per Bundle | Higher due to rigging and handling | Lower with streamlined operations |
SPBE systems combine drive, control, and hydraulic extraction in one integrated model, enhancing productivity across multiple exchangers within a single shift. The design reduces transfers, decreases operator exposure, and standardizes operational parameters. Technical data often demonstrates significantly shortened cycle times and lower total cost per bundle relative to conventional methods.
Maintenance and Longevity
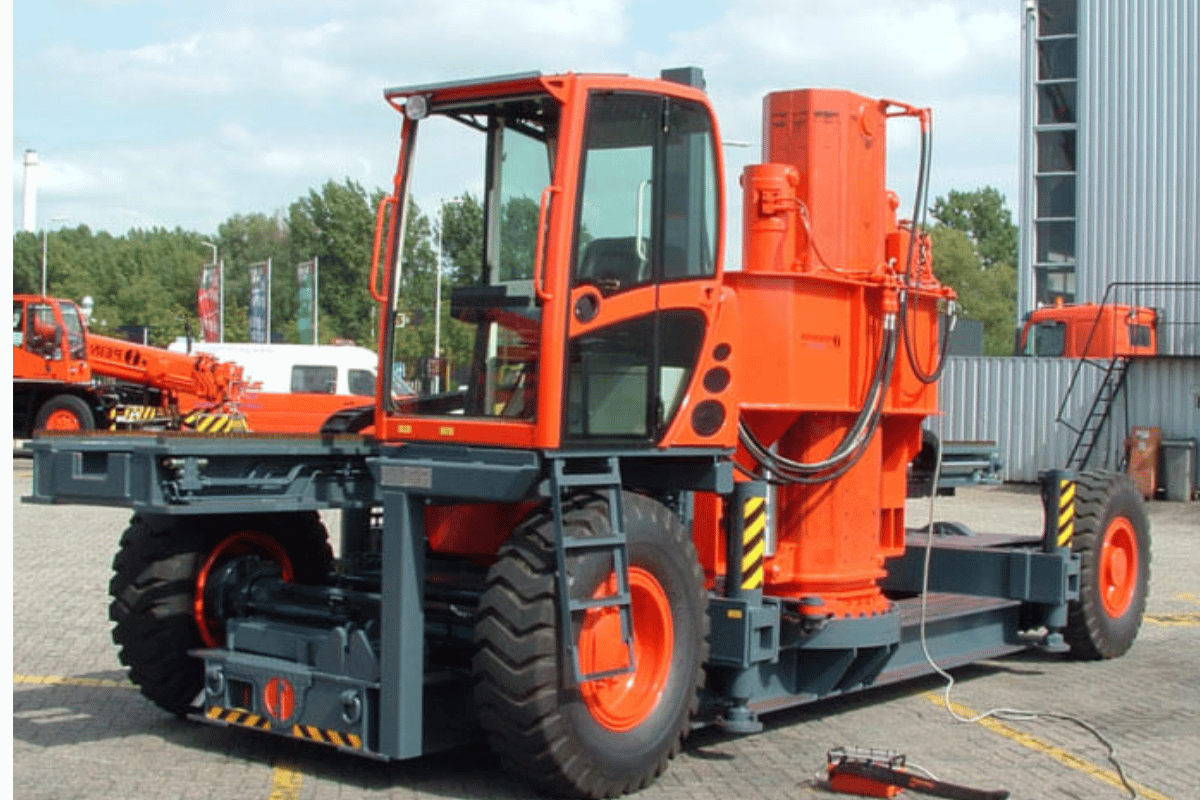

Equipment service life depends on disciplined maintenance schedules paired with design features protecting critical hydraulic components. Routine maintenance ensures equipment reliability and extends operational lifespan.
Recommend reading: Bundle Puller & Bundle Extractor Equipments
Maintenance Checklist
Daily Maintenance Tasks:
✓ Filter inspection and replacement as needed
✓ Hydraulic fluid analysis for contamination
✓ Hose and seal inspection for wear or leaks
✓ Mount bolt tightening and torque verification
✓ Control surface mating inspection
